Thermoelectric modules are used for cooling and temperature stabilization of the object that is placed on the heat-absorbing surface of the module.

Key Characteristics:
The main characteristics of the module are the dependence of the cooling capacity Q on the temperature difference ∆Т across the module. The set of dependencies Q(∆T) for different power supply currents of the module is usually called load characteristics.
The temperature difference ∆Т is determined by the temperature difference between the heat-absorbing and heat-releasing module surfaces. The cooling capacity Q corresponds to the power of heat absorbed by the module, that is, the power of the thermal load on the module.
Main Parameters
the maximum temperature difference ∆Тmax, which is reached on the module without thermal load (Q=0) at the maximum supply current Imax
the maximum cooling capacity Qmax, which corresponds to the heat load on the module at a temperature difference of ∆Т=0 and current Imax
The maximum temperature difference Tmax is proportional to the figure of merit of the thermoelectric materials Z of which the thermoelement legs are made. The Interm company produces modern thermoelectric cooling modules of the most efficient semiconductor alloys based on Bi-Te. Single-stage modules produced by the company have a value of ∆Tmax = 68 - 74°C.
The maximum cooling capacity Qmax is determined by the module structure. The company produces modules with cooling capacity from several mW to several hundred Watts.
The load characteristics Q(∆T) and the main parameters ∆Тmax and Qmax allow one to choose the appropriate module for cooling and thermal stabilization of the object.
TO SELECT A MODULE, THE FOLLOWING INPUT DATA MUST BE PROVIDED:

cooling capacity Q, which the module must provide

the temperature of the heat-absorbing (cold) surface of the module, which corresponds to the cooling temperature of the object Tc

the temperature of the heat-releasing (hot) surface of the module Th
The temperature difference ∆T=Th-Tc, which must be ensured by the module, is calculated. Based on the ∆T value, select the series whose module is intended to be used. For example, to ensure ∆T<70°С, one can choose a series of “single-stage modules”, for 70°С≤∆T≤95°С - “two-stage modules”, etc.
The formula Qmax=QΔTmax/(Tmax-T) determines the maximum cooling capacity that the module must have to ensure the specified values of the thermal load Q and the temperature difference ∆T. For Qmax calculations, the Tmax value corresponding to the selected series of modules is used, for example, for single-cascade modules, Tmax=70°C.
From the tables of the PRODUCTION section, which provide the main characteristics of the modules of the selected series, choose the module with the maximum cooling capacity exceeding the calculated value of Qmax. At the same time, the requirements for the supply current, voltage and dimensions of the module are taken into account.
The operating current of the module supply is determined, which provides the specified values of cooling capacity Q and temperature difference ∆T. To do this, use the load characteristics Q(∆T) of the selected module. The choice of operating current I is illustrated in the figure.
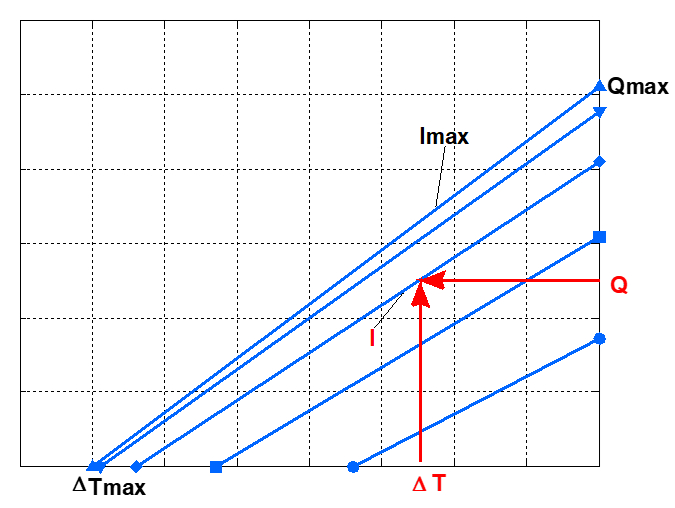
The selection of the cooling module operating current
The supply voltage of the module U is determined by the values of the operating current I and the temperature difference ∆T based on the dependence of the voltage on the temperature difference U(∆T). The selection of the module supply voltage is shown in the figure.
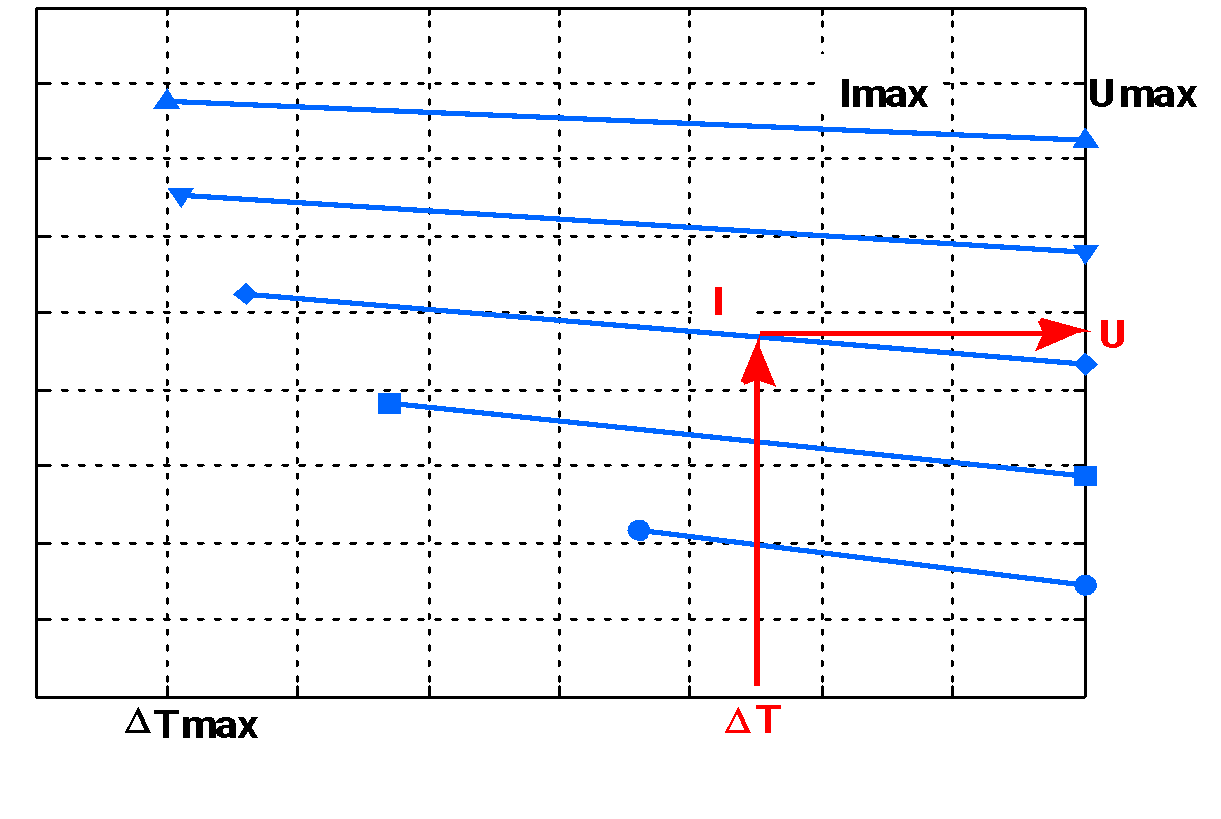
Selecting the supply voltage for the cooling module
The electric power consumed by the module is calculated by the formula W=IU
The coefficient of performance COP, which characterizes the energy efficiency of the module, is determined by the ratio COP=Q/W.
The loading characteristics Q(∆T) and dependences U(∆T) required for module selection for all modules offered by our company are listed in the PRODUCT section.